Southwest Monsoon officially ends in India with 14% deficit
September 30, 2015
New Delhi
Rainfall in the country was 14 per cent lower than normal during the Southwest monsoon that officially ended today with a double-digit rain deficit being recorded for the second consecutive year causing drought in some states.
This year’s summer rains were particularly affected by the El-Nino phenomenon with the deficiency for the four-month long season being more or less in line with the forecast of the Indian Meteorological Department(IMD) which predicted 12 per cent deficit. Last year, there was a 12 per cent deficit.
Around 55 per cent of the country, however, received “normal” rainfall, the IMD said.
The official period for the Southwest Monsoon season in India is between June 1 and September 30.
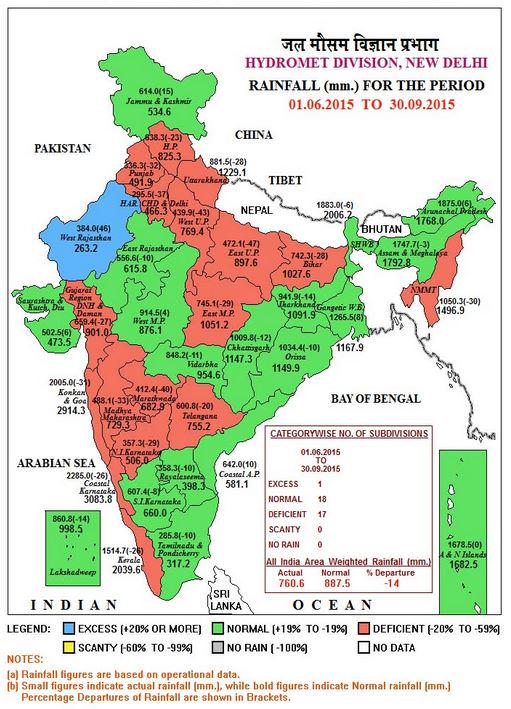
“Rainfall in Southwest monsoon was 14 per cent deficient.
We are satisfied that our Long Range Forecast have turned out as per our prediction. This was for the first time that we made a prediction of more than 10 per cent deficiency,” IMD Director General Laxman Singh Rathore said.
IMD had made a forecast of 88 per cent rainfall with plus or minus 4 per cent.
Country wise, Northwest India has recorded a deficiency of 17 per cent, followed by 16 per cent in Central India, 15 per cent in Southern Peninsula and 8 per cent in East and North-east India.
Several parts of the country also witnessed a drought like situation. For instance the deficiency in Marathwada ended at 40 per cent, but situation has particularly turned grim where the overall deficiency now stands at around 45 per cent. Incidentally, West Rajasthan, which is usually known to be arid, has received 46 per cent more rainfall this year.
The season this year witnessed rainfall, which started with excess rainfall for the first month, but ended with a deficiency in the remaining three months.
The monsoon, which hit the Kerala coast a tad late on June 5, four days after the official onset of rainy season in India. June saw 16 per cent excess rain this season. However, July witnessed deficiency of 16 per cent. It further grew to 22 and 24 per cent for August and September respectively.
Some of the states that have observed very poor rains are Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Haryana and Maharashtra, Skymet, a rival of IMD said.
With weak monsoon, India’s food grain production is also projected to drop by 1.78 per cent to 124.05 million tonnes in the 2015-16 kharif season due to poor monsoon and drought-like situation in some states like Karnataka. Food grain output was 126.31 million tonnes (MT) in the kharif (summer) season of the 2014-15 crop year (July-June).
As the season ended with a deficit, as on September 23, ninety-one major water reservoirs monitored by the Central Water Commission (CWC) filled to the extent of only 62 per cent to its total capacity of 253.388 billion cubic meter (bcm).
PTI
Recent Stories
- How to Control High Blood Pressure and Reduce the Impact of Chronic Angina
- JP Morgan sets up derivatives unit in GIFT City: Report
- Gujarat ATS, NCB, and Navy seize around 700 kg drugs from Iranian vessel off Porbandar
- All the devotees can now hoist Dwaja at Shikar of Dakor Mandir
- 47 parshads take sant diksha at Shree Lakshminarayan Dev Dwishatabdi Mahotsav in Vadtal
- 70.55% final voter turnout in Vav Assembly by-polls 2024
- Olympic 2036 bid: AMC revises TP schemes to allocate separate plots for playgrounds
