Details of Gujarat portion of Delhi – Mumbai Expressway
September 15, 2021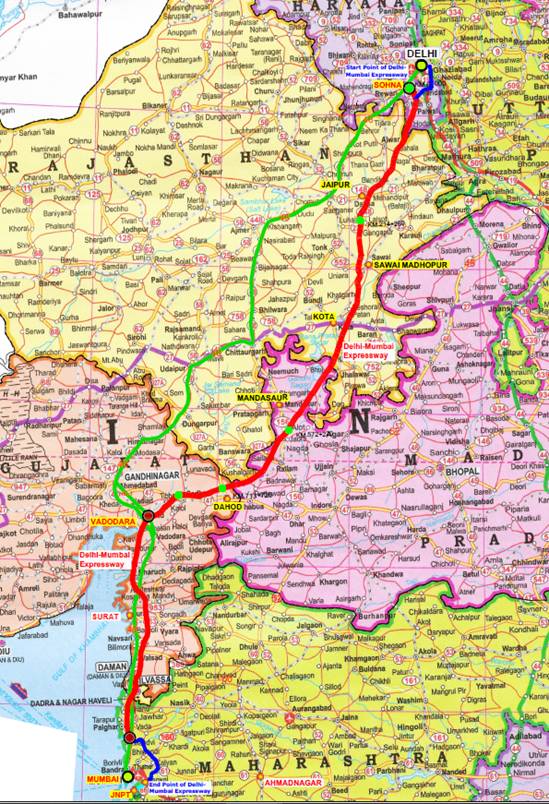
New Delhi: Union Minister for Road Transport and Highways Shri Nitin Gadkari will be reviewingthe progress of Delhi-Mumbai Expressway(DME) on 16th – 17th September covering the States of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat .Being developed at a cost of 98,000 crores, the 1380 km long Delhi Mumbai expressway will be the longest expressway in India. It will enhance connectivity between National Capital, Delhi and Financial Capital, Mumbai. The expressway will connect urban centers of Delhi through Delhi-Faridabad-Sohna section of the corridor along with a spur to Jewar Airport and Jawaharlal Nehru Port to Mumbai through a spur in Mumbai.
In addition, the expressway which passes through the six states of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Gujarat and Maharashtra will improve the connectivity to economic hubs like Jaipur, Kishangarh, Ajmer, Kota, Chittorgarh, Udaipur, Bhopal, Ujjain, Indore, Ahmedabad, Vadodara, Surat bringing economic prosperity to millions.
Delhi Mumbai Expressway, envisaged under the vision of Prime Minister’s ‘New India’, was kick started in 2018 with the foundation stone being laid on 9th March 2019. Out of the 1,380 kms, contracts for more than 1,200 kms have already been awarded and is under progress.
Gujarat Portion Details(Location 5/6)
- Length in State: 423 km of the expressway is built across the state of Gujarat at a total capital cost of more than 35,100 crores with contracts for 390 kms already awarded and remaining package to be awarded shortly. Two sections of the corridor, Delhi – Vadodara Section and Vadodara Mumbai Section will pass through the state.
- Connectivity: Gujarat is a key economic hub of the country and multiple interchanges have been planned across the state to provide connectivity to the towns and cities of Dahod, Limkheda, Panchmahal, Vadodara, Bharuch, Surat and Valsad. The expressway will also be connected to the state capital through the Vadodara – Ahmedabad Expressway. 60 major bridges, 17 interchanges, 17 flyovers and 8 RoBs have been planned across the state of Gujarat.
- Marquee Feature:
- One key feature of the corridor in the state of Gujarat is the innovative pavement design planned with perpetual design in the Delhi – Vadodara section and rigid pavement design for the Vadodara – Mumbai section based on the climatic conditions to maximize the economic lifetime of the expressway.
- An iconic bridge built across the Narmada river near Bharuch. The 2km long extradosed cable span bridge will be India’s first 8 lane bridge to be built across the expressway. This, along with the iconic interchange near the city of Bharuch expected to refresh the face of the expressway development in the country.
- WSA: 33 WSAs are being planned to be built across the state of Gujarat to provide world class amenities to commutes as well as generate employment opportunity in the state.
- Completion Schedule: One key section of the overall expressway, the Vadodara – Ankleshwar section of 100 km is in advanced stages of construction and targeted to be open to traffic by March 2022. The remaining section from Ankleshwar to Talsari is targeted to be completed by Mar 2023.
Overall Corridor Completion Schedule
The two sections of the expressway, the Delhi – Dausa – Lalsotsection which is part of the Delhi-Jaipur Expressway and the Vadodara-Ankleshwar Section which connects Vadodara to the economic hub of Bharuch are likely to opened for traffic by Mar’ 2022The complete expressway is planned to be completed by Mar’ 2023.
The key challenges during the pre-construction stage were extensive land acquisition and timely clearances such as environment, forest and wildlife. Land acquisition for an area of 15,000 ha. was completed in short span of time with land acquisition for Delhi to Vadodara section completed in less than 1 year. In addition, the statuary clearances were obtained in parallel to save time during implementation.
To ensure faster implementation, use of technology was promoted through-out the project lifecycle where advanced technologies such as LiDAR, GPR, Digital maps were used during the preparation of Detailed Project Report followed by use of Drone based surveys, Equipment telematics, pre-casting during the construction stage. Additionally, the packaging of the construction was also planned scientifically to minimize overrun of time through intelligent tendering processes which enabled simultaneous working at multiple stretches. PIB
Related Stories
Entry and exit points of new Vadodara - Bharuch expressway explained
Farmers in South Gujarat get far better compensation over land acquision for expressway project
દિલ્હી-મુંબઇ ગ્રીન એક્સપ્રેસ વે વડોદરા માટે વિકાસની નવી શક્યતાઓના દ્વાર ખોલશે
Protest against Delhi - Mumbai Expressway, Dahod Smart City Project voiced in Gujarat Congress function
Delhi - Mumbai Expressway to complete by 2023: Gadkari in Gujarat
Delhi - Mumbai Expressway: Gadkari inspects India's first 8 lane expressway bridge to come up in Gujarat
Delhi-Mumbai Express Way: Nitin Gadkari in Gujarat today
Recent Stories
- ACB Gujarat nabs police constable in ₹25000 bribe case
- IMD issues Orange and Yellow alerts for parts of Gujarat for next 48 hours
- Ahmedabad–Baku direct flight service to begin in July
- Vadodara DEO bars private schools from pressuring parents to buy uniforms, books from campus vendors
- Gujarat Medical Council suspends licence of a Doctor
- Goods vehicles allowed on Commod Circle–Torrent Power Station stretch in Ahmedabad
- Traffic Diversion, No-Parking Zones Announced in Vadodara for Parshuram Jayanti Procession
